Are you trying to watch the Champions League final, schedule a crucial meeting with a team in Berlin, or book your dream flight to Rome? If so, you’ve certainly come across the acronym CEST.
We dug deep to demystify CEST, explain why it's vital for you in Mexico, Colombia, or Argentina, and even uncover the incredible story of how a dictator changed time in Europe forever.
What Does CEST Mean? The Quick and Direct Answer
For those in a hurry, here’s the clear and straightforward answer you need:
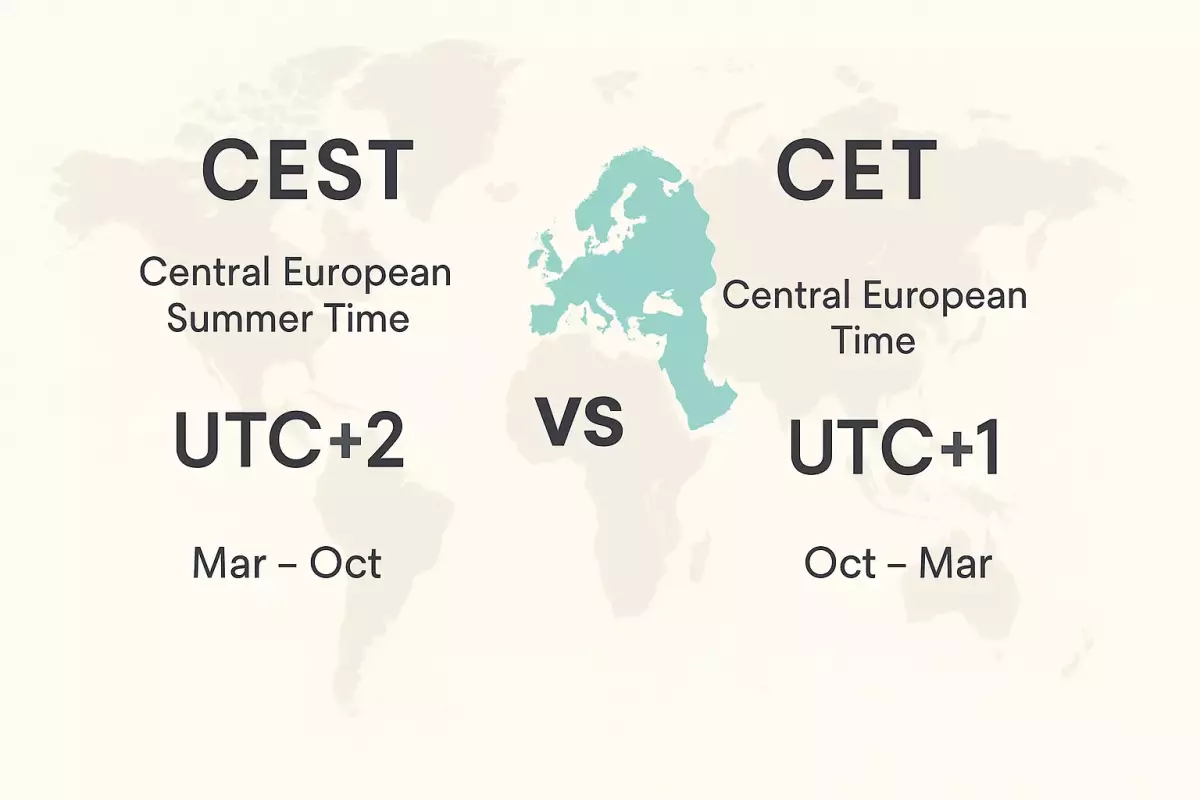
- CEST (Central European Summer Time): It is the Central European Summer Time, corresponding to UTC+2. It is the time zone that most Central European countries use during the summer months to take advantage of sunlight.
- CET (Central European Time): It is the Central European Standard Time, corresponding to UTC+1. It is the "normal" or winter time zone for the same regions.
In summary: Europe uses CET in the winter and moves the clock forward one hour to CEST in the summer.
Difference Between CEST, CET, and Other Time Zones: Simple Explanation and Comparative Tables
There is frequent confusion between the acronyms CET, CEST, UTC, and GMT. After all, what really changes? CET (Central European Time) indicates the "normal" time of Central Europe, used from the end of October to the end of March (UTC+1). CEST is activated in the European summer, adding one hour (UTC+2).
To make it even clearer, check the comparative table:
| Acronym | Name | UTC Offset | Usage Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| CET | Central European Time | UTC+1 | Winter |
| CEST | Central European Summer Time | UTC+2 | Summer |
| GMT | Greenwich Mean Time | UTC+0 | Global Reference |
| UTC | Coordinated Universal Time | UTC+0 | Technical Reference |
Additionally, there are other variations such as WET (Western European Time), BST (British Summer Time), EET (Eastern European Time), and WEST (Western European Summer Time). Like CEST, each of these acronyms indicates a distinct official time, impacting international schedules.
| Feature | CET (Central European Standard Time) | CEST (Central European Summer Time) |
|---|---|---|
| UTC Offset | UTC+1 (One hour ahead of UTC) | UTC+2 (Two hours ahead of UTC) |
| Usage Period | End of October to end of March | End of March to end of October |
| Purpose | Standard winter time | Summer time for energy saving |
| Example | When it’s 12:00 UTC, it’s 13:00 CET | When it’s 12:00 UTC, it’s 14:00 CEST |
When CEST Starts and Ends from 2025 to 2030
The time change in Europe, known as Daylight Saving Time (DST), was standardized by the EU to save energy and simplify logistics. Since 1996, the European Union synchronizes the changes for all participating countries, minimizing confusion in travel and business.
The rule is simple:
- Start of CEST: On the last Sunday of March, at 01:00 UTC, clocks move forward to 03:00 CEST.
- End of CEST: On the last Sunday of October, at 01:00 UTC, clocks move back to 02:00 CET.
Although there’s an ongoing debate to end this practice, it remains in effect. Use this table to plan years in advance.
Time Change Dates Table in Europe
| Year | Start of CEST (Change to UTC+2) | End of CEST (Return to UTC+1) |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | Sunday, March 30 | Sunday, October 26 |
| 2026 | Sunday, March 29 | Sunday, October 25 |
| 2027 | Sunday, March 28 | Sunday, October 31 |
| 2028 | Sunday, March 26 | Sunday, October 29 |
| 2029 | Sunday, March 25 | Sunday, October 28 |
| 2030 | Sunday, March 31 | Sunday, October 27 |
Impact of CEST in Real Life: Business, Sports, Tourism, and Education
The application of CEST goes far beyond theory. For technology professionals, traders, students, and tourists, understanding the difference between CET and CEST is crucial.
- International Business: Meetings scheduled in CEST may occur at unfavorable times for those in Latin America. For instance, a meeting at 09:00 in Paris (CEST) corresponds to 04:00 in Buenos Aires (ART), 02:00 in Lima (PET), and 01:00 in Mexico City (CST).
- Trading and Markets: Exchanges like Deutsche Börse and Madrid Stock Exchange operate in CET/CEST, directly impacting Forex operations and international stocks.
- Global Sports: Competitions like the UEFA Champions League and Formula 1 use CEST in their official calendars. Thus, correctly adjusting times prevents missing broadcasts or participating late in real-time discussions.
- Tourism and Exchange: Flights, hotel bookings, and excursions, as well as online classes at universities like Sorbonne University, follow CET/CEST. Properly planning times eliminates confusion in travel and studies.
As the examples above show, converting times is not just a matter of convenience, but of avoiding losses, delays, and missed opportunities.
How to Convert CEST to Local Time: Quick Methods and Essential Tools
Before you schedule your next international meeting or buy tickets for a European show, know that converting CEST to your local time can be simple with the right tools.
Time Zone Converter.
Convert multiple times between cities around the world with absolute precision. The ultimate tool for scheduling global meetings and events without stress.
Convert Hours Accurately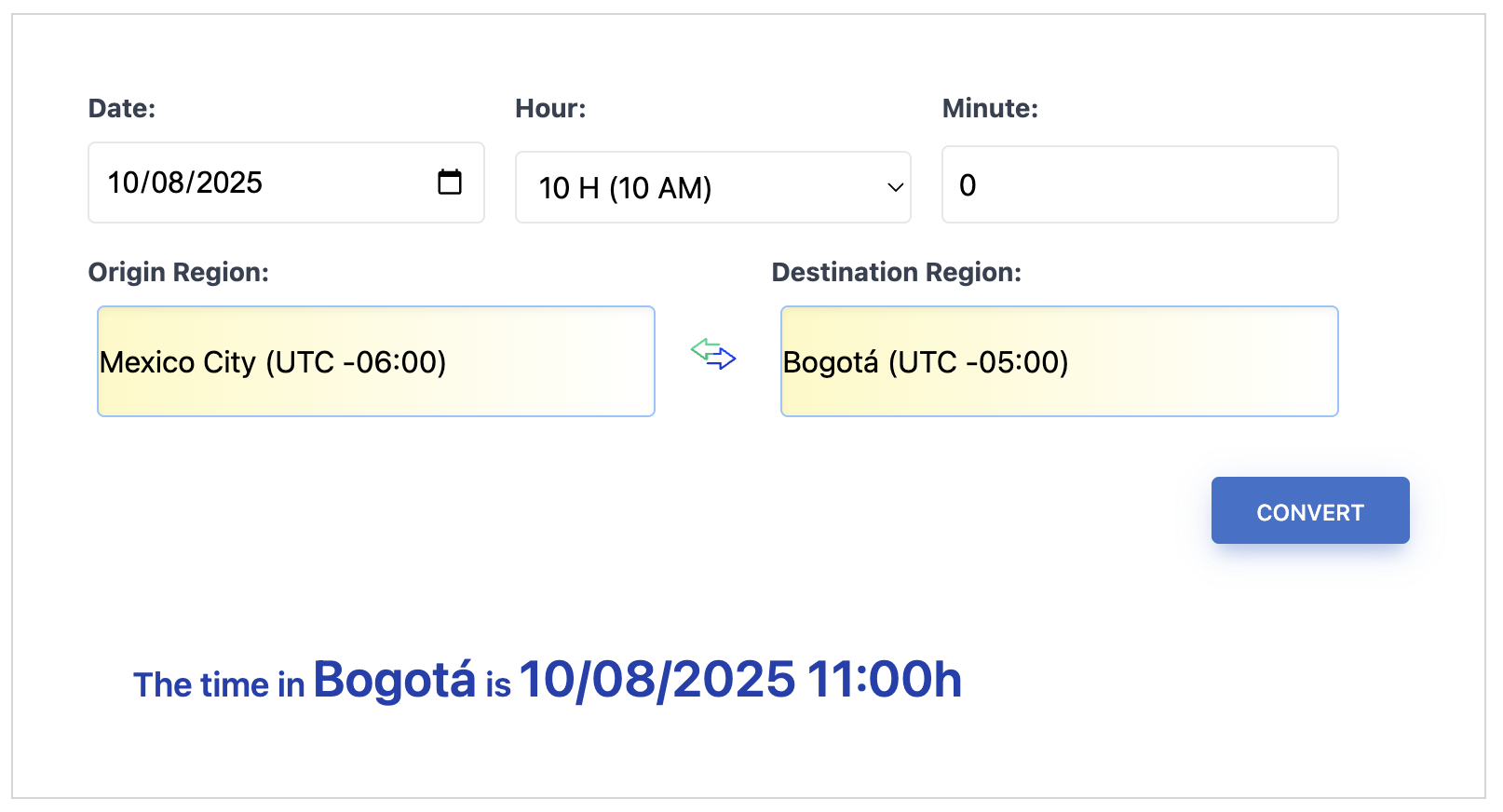
Moreover, the table below illustrates the main time differences between Europe and Latin America during the CEST period:
| Time in CEST | Mexico City (CST) (click here) | Bogotá/Lima (COT/PET) (click here) | Buenos Aires (ART) (click here) | Brasília (BRT) (click here) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 03:00 | 03:00 |
| 14:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 09:00 | 09:00 |
| 21:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 16:00 | 16:00 |
In conclusion, before scheduling any international commitment, always use our time zone converter or adjust your digital calendar according to the official time zone of the event.
Which Countries Use CEST and CET?
Below, check the list of the main countries and territories that use CET in winter and CEST in summer. Note how political definition can override geography, as seen in Spain and France.
| Country | CET (Winter) | CEST (Summer) |
|---|---|---|
| Germany | Yes | Yes |
| France | Yes | Yes |
| Spain (except Canary Islands) | Yes | Yes |
| Italy | Yes | Yes |
| Poland | Yes | Yes |
| Netherlands | Yes | Yes |
| Switzerland | Yes | Yes |
| Belgium | Yes | Yes |
| Croatia | Yes | Yes |
| Czech Republic | Yes | Yes |
| Hungary | Yes | Yes |
| Luxembourg | Yes | Yes |
| Norway | Yes | Yes |
| Denmark | Yes | Yes |
| Sweden | Yes | Yes |
| Others (Andorra, Monaco, Liechtenstein, Vatican, San Marino) | Yes | Yes |
Consequently, many international booking systems and banks strictly follow these conventions to ensure synchronization in critical operations.
The Incredible Story of the Spanish Time Zone
Why does Spain, geographically aligned with London, share the same time zone as Berlin? The answer is a fascinating story of politics, war, and inertia.
- The "Correct" Time: Until 1940, Spain operated in the same time zone as its geographical neighbor, Portugal (GMT/WET).
- The 1940 Decision: During World War II, General Francisco Franco moved the clocks forward by one hour. This decision is widely seen as a political gesture aligning with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy, which operated on CET.
- The Clock That Never Went Back: After the war, other countries like the United Kingdom returned to their natural time zone. Spain, due to political inertia, never did.
- The Modern Consequences: This anomaly explains Spain's famous late meal times and its nightlife lifestyle. When a clock in Madrid shows 22:00, the sun (and the biological clock) is still closer to 21:00. The debate about returning to the "correct" time zone continues to this day.